Imagine putting two white lights of different hues side by side. Wouldn’t you find this inconsistent light color strange and visually unpleasant? To avoid such failures in lighting, it is important to consider SDCM. It measures the color consistency of light and ensures uniform, perfect light output.
Get ready to explore all about SDCM and choose the right LED strip lights for your project.
What is SDCM?
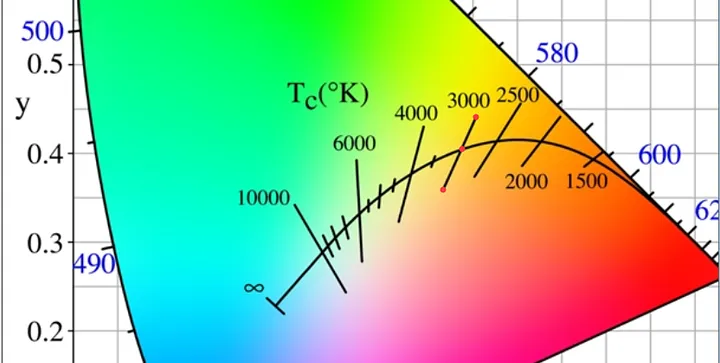
SDCM stands for “Standard Deviation Colorimetric”. It measures color and determines how closely one color matches another. It uses the same principle as MacAdam ellipses to measure the color consistency of a light source.
Two lights will never be exactly the same color. But you can’t always detect this difference. There is a level of color tolerance where the human eye can’t detect these differences. You can detect the color source of the light through MacAdam ellipses.
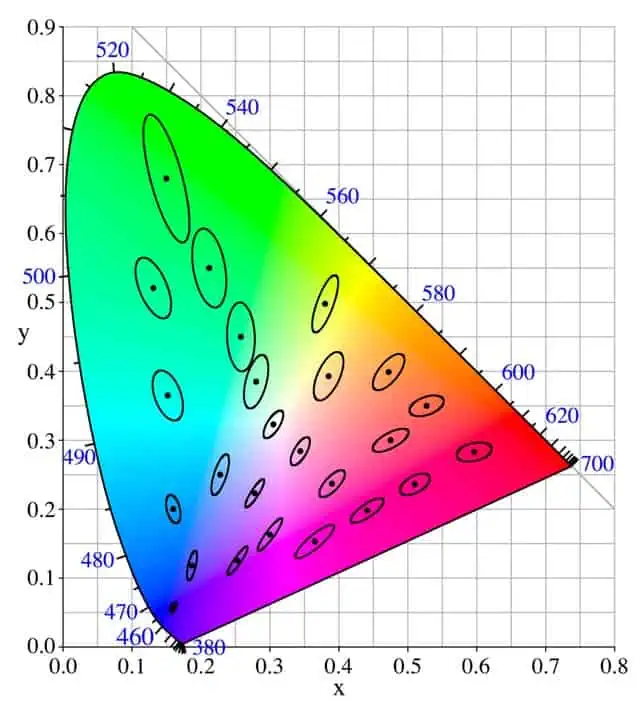
The ellipse is divided into several SDCM steps according to the distance from the target color. For the lower steps, no or little color difference is noticed. For the higher steps, your naked eye can recognize the color difference between the light sources.
| MacAdam ellipse (SDCM) | Visibility |
| 1 SDCM | Almost no visible deviations |
| 2 SDCM | Deviations are visible only with instruments |
| 3 SDCM | Few deviations visible with the human eye |
| 4 SDCM | Visible deviations |
| 5 SDCM | Strongly visible deviation |
Understanding SDCM with Examples
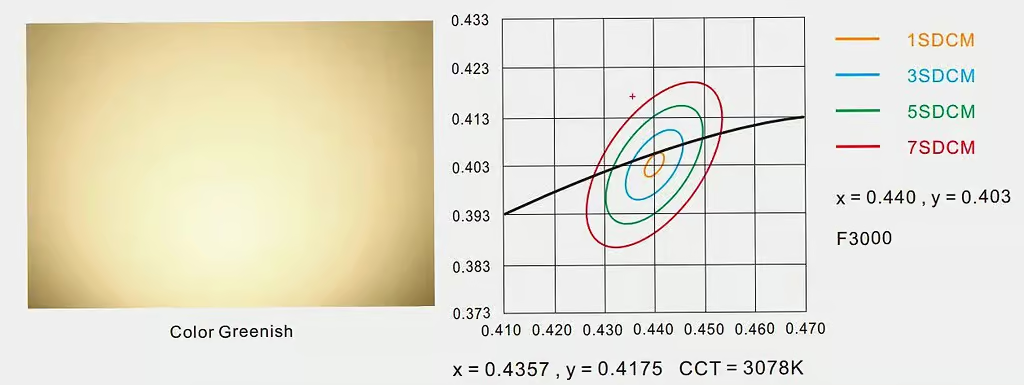
Have you ever bought two lamps with the same CCT, but when you turn them on, they seem to have different colors? This is nothing to be surprised about. This can happen due to the difference in SDCM. Let me explain more clearly with an example.
Suppose you have two lamps with a 3000K CCT. However, one is SDCM 2, while the other is SDCM 5. The lamp with 2 SDCM will display the same 3000K color, which is warm white. Meanwhile, a higher SDCM, such as 5 or higher, will differ in color consistency and saturation. Therefore, with the difference in SDCM, you will see that the 3000K light appears green or red.
Practical Application of SDCM
When buying any lamp, the common indicators we compare are CCT and CRI. But the problem is that only these two facts cannot ensure the color consistency of the light. As I discussed in the example above, two lamps with the same CCT may end up appearing different due to the SDCM value. So, to ensure color consistency, you have no choice but to skip the SDCM.
Typically, indoor spaces or applications where the color needs to be accurately maintained require less SDCM. This ensures color consistency and your space lighting is compact. Generally speaking, it is best to use the first 2 SDCM for indoor lighting. However, in outdoor spaces, lamps with more color derivatives can also be OK. You can choose 5 SDCM or higher depending on the lighting requirements.
| Application | Suggested SDCM |
| Art Galleries and Museums | 1-2 SDCM |
| Healthcare Facilities | 1 – 2 SDCM |
| Residential Spaces | 1 – 3 SDCM |
| Office Spaces | 3 – 4 SDCM |
| Manufacturing and Industrial | 4 – 5 SDCM |
| Outdoor Lighting | 5 or higher SDCM |
Importance of SDCM in LED Strip Lights
Consistency and Uniformity of Color
Low SDCM is essential to maintain color consistency. This ensures that the light source looks the same. So when you buy lighting for a museum, art gallery, or similar application with high color consistency requirements, look for low SDCM lamps.
Visual Comfort
Lights with high SDCM look very different when placed side by side. Such lighting will naturally give any visitor the idea that the lighting is set up wrong. This inconsistent lighting creates glare issues and makes you feel uncomfortable. So it is important to use low SDCM lamps to get smooth and uniform lighting.
Maintaining the Quality of LED Chips
Manufacturers use SDCM as a standard to maintain color consistency of light. Therefore, all chips emitted are the same color. Therefore, the lighting of LED strips looks flawless due to color consistency. Therefore, considering SDCM values can improve the quality of the final product.
Long-term Performance
The color of a lamp will gradually change over time. So, with high SDCM lamps, the change in light will be more noticeable. On the contrary, if low SDCM lamps are used, it will minimize the color variation issues. Therefore, you can use the lamp for a long time without replacement.
Guide to Buying the Right LED Strip Light
In applications such as museums, theaters, galleries, and commercial lighting, you must strictly follow color consistency. In this case, SDCM will guide you to choose the right LED strip light. For lighting areas where visual appearance is critical, use low SDCM lamps. 1 to 3 SDCM works well. Likewise, SDCM is not a major issue for outdoor lighting. You can choose a higher SDCM rating.
What factors affect the SDCM of LED strips?
Using inferior materials
It is normal for the color of light to change gradually with aging. However, using inferior materials can cause premature color changes in LED chips. As a result, the SDCM value quickly rises above normal levels, and the light color no longer remains constant. Likewise, the heat capacity is reduced with the use of inferior materials. This causes the lamp to overheat and cause color changes due to changes in SDCM.
Changes in driving current
The flow of current affects the color output of light. In fact, when the current inside the LED chip increases, the temperature of the diode also increases. This changes the emission of the color spectrum, which causes color changes. This is why the SDCM also becomes high. In addition, frequent changes in driving current affect the service life of the lamp.
Incorrect installation
The operating temperature has a greater impact on the SDCM. When there are not enough heat dissipation facilities in LED strips, they overheat. Due to the increase in temperature, the CCT also increases. Therefore, the warm color of the light tends to produce a bluish hue. Increased color temperature causes changes in SDCM.
Use of diffusers
You often use diffusers with LED strips. They act as a cover for the LED light. That is, the light passes through the diffuser before being diffused into the surrounding environment. This causes the color derivative and SDCM of the final light output to vary. Therefore, the LED strip you purchase
How to reduce the color tolerance distance? : Reduce SDCM
You can follow the following three methods to reduce the SDCM value and achieve the target light color:
1. Color mixing method
The color mixing method is an effective way to reduce the SDCM and match the target color. Here, you need to select two or more LED chips from the factory’s color separation pie or color bin. Then, mix them in equal or unequal proportions to make the SDCM closer to the target light source.
2. Adjust Bin Center Method
White LEDs usually use phosphor coating. By adjusting the proportion of phosphor, you can move the center point in the opposite direction. Therefore, the SDCM will be reduced and closer to the target light color.
3. Hot Box Method
In the hot box method, you have to increase the operating junction temperature while color separation. The temperature should be equal to the operating temperature of the LED. In this way, by increasing the operating junction temperature, the SDCM will be greatly reduced. For more information, you can check out What is LED binning?
What is color temperature?
Color temperature describes the color of any light source. It compares the color of a black body radiator to the light source. When a black body is heated, it changes color as the temperature increases. The color sequence is as follows:
Dark red → light red → orange → white → blue
The temperature at which the black body color matches the color of the light source is the color temperature of the light. For example, a 3000K black body appears warm yellow-white. Similarly, a light source with a color temperature of 3000K also appears the same color.
In traditional lamps such as incandescent lamps, the color temperature varies greatly, about 150K. Therefore, you can visually detect the color change. However, in LED lamps, the color temperature change may be only 15K.
What is Correlated Color Temperature (CCT)?
Correlated Color Temperature (CCT) measures the hue of white light in Kelvin. The higher the CCT, the cooler the light, and the lower the CCT, the warmer the light.
| CCT | Light Color |
| 2700K | Warm white |
| 3000K | Soft white |
| 3500K | Neutral white |
| 4000K | Daylight white |
| 5000K and above | Crystal white light |
However, even with a certain CCT, you can still find noticeable differences in light color. For example, a bulb with a CCT of 3000K may appear green, warm white, or red. Even with these color differences, they are still called 3000K bulbs. Therefore, it can be said that CCT is basically a range of color temperatures over which the color temperature value fluctuates.
So, how do you identify the exact color of light? To detect the exact color of light, you need to consider SDCM.
What is the relationship between SDCM and CCT?
The change in CCT is related to the shift in SDCM steps. This is why two light sources of the same CCT may appear different in color.
Let me explain the relationship between CCT and SDCM with an example. Let’s say you buy two lamps with a standard 3000K CCT rating. However, the two lamps may appear different due to the difference in SDCM.
- 1st Light With Low SDCM: <5

- 2nd Light With High SDCM: >7

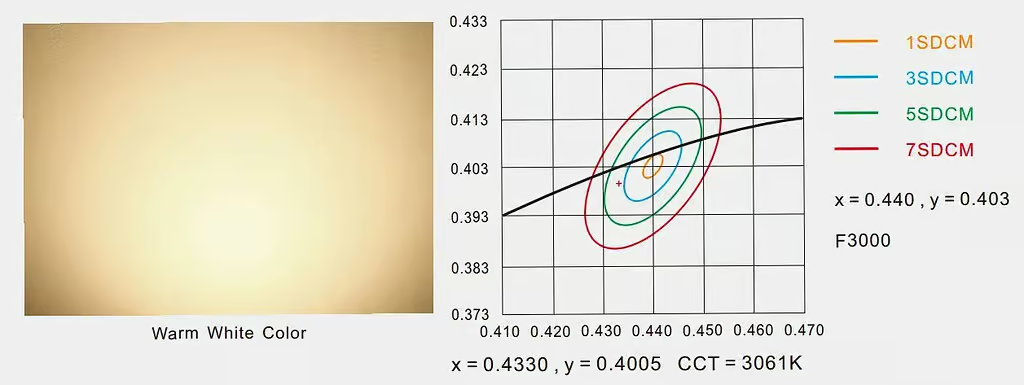
The SDCM of the second lamp is far from the target point. It exceeds the 7SDCM step and has a greenish color. Its CCT rating is 3078K.
Even though the CCT change is only 17K, the color output of the two lamps is very different due to the large SDCM difference.
What are the advantages of high CRI and low SDCM?
CRI is another metric related to light color. It determines the color accuracy of an object under artificial lighting. It is graded from 0 to 100. A high CRI means that the color of an object under a lamp is closer to natural light.
In contrast, SDCM determines the color shift of light compared to another target light source. Low SDCM means less color shift and similar color output. Therefore, lamps with high CRI and low SDCM result in high-quality lighting. The following benefits can be obtained by using these lamps:
- Higher color accuracy
- Color consistency and uniform lighting
- No glare issues, which reduces eye fatigue
- Comfortable visual effects
In addition, high CRI and low SDCM lamps are essential for commercial lighting. In retail stores, high CRI lamps show accurate product colors to customers. Similarly, when shopping under low SDCM lamps, you will get a comfortable and uniform light setting.
SDCM and Color Difference: Difference and Relationship
SDCM compares the difference between the X and Y values of a light source and the X and Y values of a standard light source. The smaller the difference, the lower the SDCM, indicating a closer match to the target light color.
In contrast, color difference refers to the difference in light color. It measures the difference between the X and Y coordinate values of two light colors. The smaller the difference, the lower the color difference. That is, the color difference is minimal, so they look similar.
Difference between SDCM and Color Difference
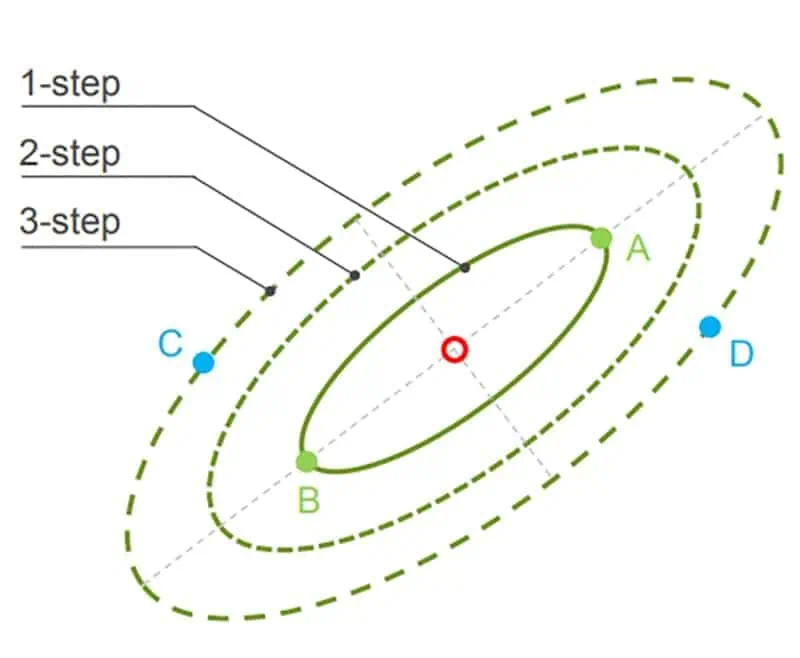
The two terms, color difference and SDCM, are different. Let’s consider an example to understand their difference. Here, we take four light sources – A, B, C, and D as samples. Their X and Y coordinate values and SDCM are as follows:
| Example For Explanation | ||
| Light Source | Value Of X | Value Of Y |
| A | 0.3856 | 0.3876 |
| B | 0.3757 | 0.3728 |
| C | 0.3801 | 0.3860 |
| D | 0.3826 | 0.3917 |
Now, let’s use the X and Y values to find the SDCM and color difference of these illuminants:
SDCM of illuminants A, B, C, and D
Putting these values on a color difference chart, we can find their SDCM as follows:
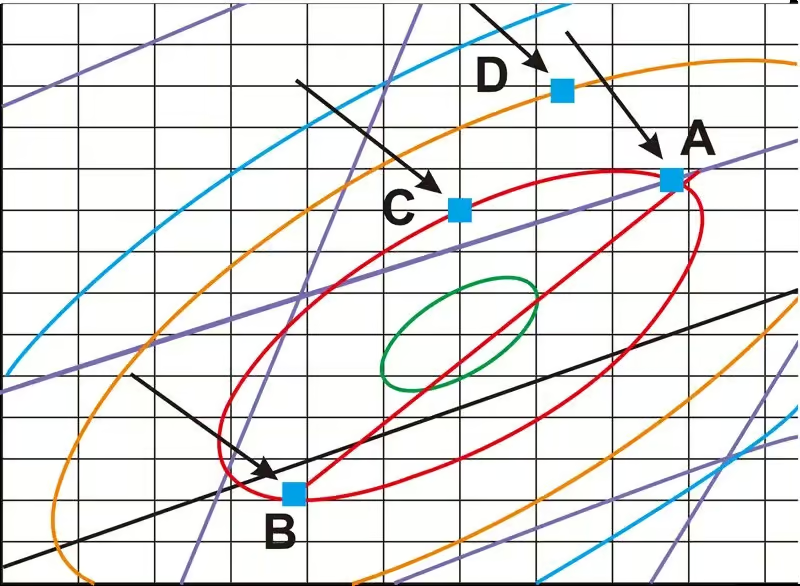
Fig: SDCM steps for light sources A, B, C, and D.
| Light source | SDCM |
| A | 3 |
| B | 3 |
| C | 3 |
| D | 5 |
Chromatic aberration for the light sources:
- Chromatic aberration of A & B
Subtracting the X and Y value of B light source from A,
X-axis = (0.3856 – 0.3757) = +0.0099
Y-axis = (0.3876 – 0.3728) = +0.0148
So, the chromatic aberration of A-B is (X=+0.0099, Y=+0.0148)
- Chromatic aberration of A & D
Subtracting the X and Y value of the D light source from A,
X-axis = (0.3856 -0.3826) = +0.0030
Y-axis = (0.3876 -0.3917) = -0.0041
So, the chromatic aberration of A-D is (X=+0.0030, Y=-0.0041)
Therefore, it can be seen that the difference in color difference between A and B is greater than that between A and D. This means that the difference between A and B is more prominent and more obvious than the difference between A and D.
Similarly, the SDCM of A and B are both 3, so they have color consistency. At the same time, in the A and D light sources, the SDCM of D is two levels higher than that of A. This means that A and D do not maintain color constancy. Therefore, comparing SDCM and color difference, you can conclude that the two terms are completely different. But what is the relationship between them?
Relationship between SDCM and color difference
You can understand the relationship between SDCM and color difference through McAdam’s experiment. The following figure shows the different SDCM steps in the MacAdams ellipse at 3000K color temperature:

Here you can see that for the 2nd order MacAdam ellipse, there is almost no chromatic aberration or color difference observable. However, for 3 SDCM, you can slightly notice the color abbreviation. Likewise, the chromatic aberration becomes more prominent in 5 and 7.
Therefore, you can find the relationship between these two terms because when the SDCM increases, the chromatic aberration also increases. Therefore, the difference between the two light sources is more noticeable.
What is Duv?
Duv stands for “Delta UV”. It is another matrix for LED lights that represents the change in light color from pure white in the chromaticity diagram. This refers to whether the white light has a green or pink tint.
The value of Duv can be positive or negative. When the chromaticity point of the light source is above the Planckian locus, it is a positive Duv. Similarly, when the point is below the Planckian locus, it is a negative Duv.
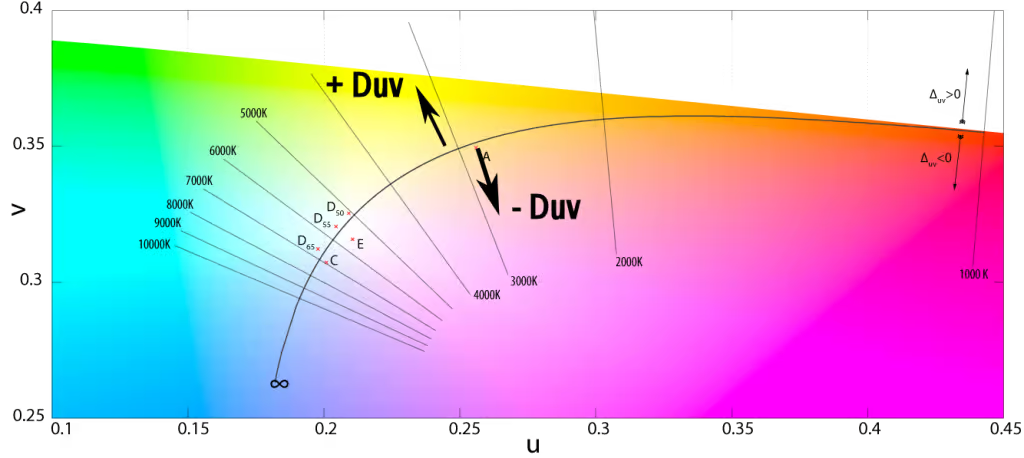
| Duv | Value | Tint & Tone |
| Positive Duv | Above zero | Greenish tint with a cool tone |
| Negative Duv | Below zero | Pinkish tint with a warm tone |
When the Duv value is above zero, it is called positive Duv. The light color appears cooler and has a green tint. Similarly, when the Duv is below zero, the light appears to have a pink tint and is warmer.
Therefore, for accuracy, you should always select a zero Duv. This ensures that the color does not deviate from the ideal CCT appearance.
Same CCT and SDCM, but different Duv
Lights with the same CCT and SDCM may look different due to different Duv values. For example, let’s take two LED lights with 4000K CCT and SDCM 1. Assume that one light has a positive Duv of +0.003, while the other has a negative Duv of -0.003.
Now, although the CCT and SDCM are the same, the light with a positive Duv will appear green. Meanwhile, the light with a negative Duv will appear warmer pink. Therefore, considering the Duv value is essential to maintain light consistency.
Note: For a balanced and accurate CCT, always choose zero Duv and low SDCM.
SDCM Standards in the LED Industry
1. North American Energy Star Standard
The North American Energy Star Standard is commonly known as Energy Star ANSI C78.377. According to this standard, the color tolerance level is ≤ 7 SDCM.
| Color Temperature Range | ANSI C78.377 | |||||
| 3 Steps | Distance | 5 Steps | Distance | 7 Steps | Distance | |
| 2700K | 2670-2780K | 110 | 2630–2830K | 200 | 2580–2880K | 300 |
| 3000K | 2970–3120K | 150 | 2920–3170K | 250 | 2870–3220K | 350 |
| 3500K | 3360–3560K | 200 | 3300–3650K | 350 | 3230–3730K | 500 |
| 4000K | 3860–4110K | 250 | 3770–4220K | 450 | 3680–4330K | 650 |
| 5000K | 4860–5210K | 350 | 4750–5300K | 550 | 4650–5450K | 900 |
| 6500K | 6300–6800K | 500 | 6150–6950K | 800 | 6050–7150K | 1100 |
2. EU IEC Standard
Luminaires should comply with EU IEC 60081:1997 standard in order to sell luminaires in Europe. According to this standard, the color difference is ≤ 6 SDCM.
| Color Temperature Range | IEC 60081 | |||||
| 3 Steps | Distance | 5 Steps | Distance | 7 Steps | Distance | |
| 2700K | 2680-2790K | 110 | 2640–2840K | 200 | 2590–2890K | 300 |
| 3000K | 2865–3015K | 150 | 2820–3070K | 250 | 2770–3120K | 350 |
| 3500K | 3350–3550K | 200 | 3280–3630K | 350 | 3210–3710K | 500 |
| 4000K | 3910–4160K | 250 | 3820–4270K | 450 | 3740–4390K | 650 |
| 5000K | 4810–5160K | 350 | 4720–5270K | 550 | 4620–5420K | 900 |
| 6500K | 6200–6700K | 500 | 6100–6900K | 800 | 5950–7050K | 1100 |
3. China GB Standard
The Chinese standard GB 10682-2002 is designed for fluorescent lamps. According to this standard, the color tolerance is ≤ 5 SDCM. This can also be used for LED lamps.
Impact of international standards on SDCM
Differences in CCT ranges
From the ANSI and IEC charts above, you can see the differences in CCT ranges for different SDCM steps. The main differences are between 2700K, 3000K, and 6500K. Therefore, when considering the color tolerance level, always consider the standard you follow.
More accurate color selection
When customers refer to CCT with SDCM steps, you get guidance to provide them with accurate light color. For example, according to European standards, customers need a lamp of 3000K-3300K with SDCM less than 5.
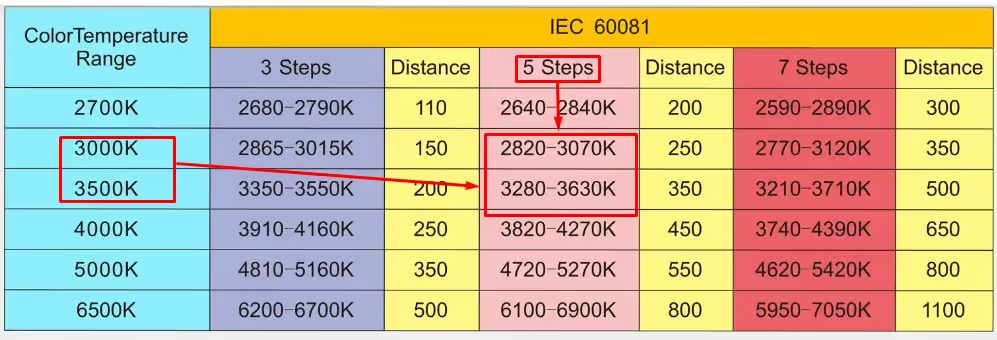
Now, according to IEC 60081 standard, 3000K-3300K for 5-step SDCM falls into two ranges. For 3000K, it is (2820-3070K). Here, you will get a CCT option of only 70K (3000K-3070K). Similarly, for 3500K, the 5-step range is 3280-3630K. Here, the CCT variation option is only 20K (3280-3300K). So, the light you give to your customers must fall into this range.
Machine differences cause SDCM offset issues
The color of lights from two manufacturers may look different even when using the same SDCM. This may be due to different machine standards, which causes the center point to shift. Therefore, the color may look different even when using the same SDCM.